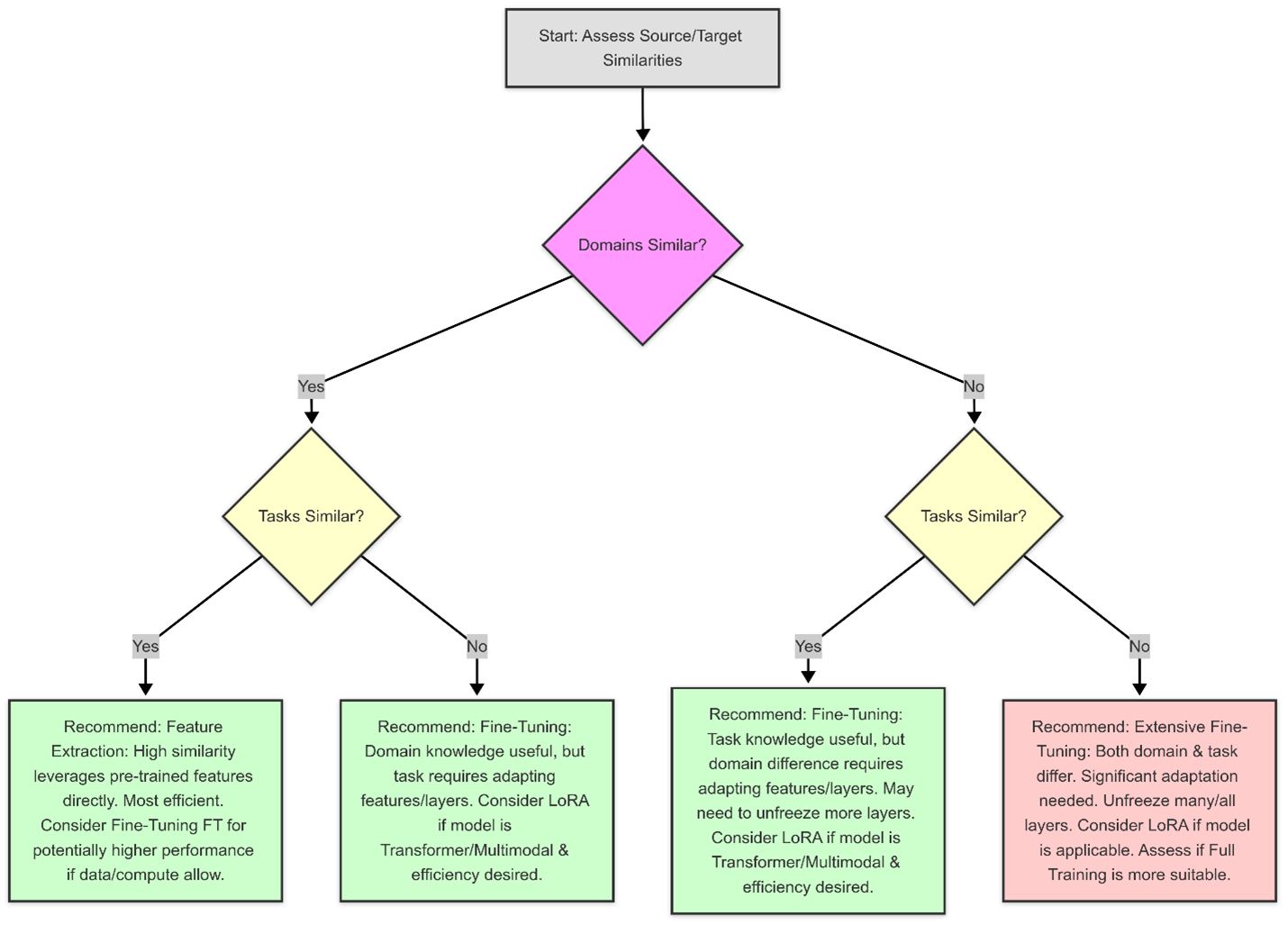
When selecting a transfer learning approach, consider the following criteria:
- Computational Efficiency: Feature extraction is less computationally intensive than fine-tuning, while LoRA is an efficient alternative for adapting large models.
- Data Availability: Fine-tuning is most beneficial when a large dataset is available, while feature extraction and LoRA perform well on limited data.
- Task Complexity: If the new task is significantly different from the original training data, fine-tuning or LoRA may be necessary to adapt representations effectively.
- Model Adaptability: LoRA is best suited for large transformer-based and multimodal models, while feature extraction and fine-tuning work well across a variety of architectures.
- Training Time: Feature extraction requires the least training time, while fine-tuning and LoRA require more time but provide better adaptability.
By evaluating these factors, practitioners can make informed decisions on the best approach for their specific application, balancing computational efficiency with model performance. Below is a quick flow chart to assist with your decision making.