
Topics
Objectives
By the end of this module:
- Students will be able to describe the key technologies needed for hands-on AI applications.
- Students will be familiar with the computational demands of AI applications and the need for HPC environments with GPUs for AI model development and deployment.
- Understand some ethical considerations concerning HPC use (or lack thereof).
Watch
Jupyter Notebooks
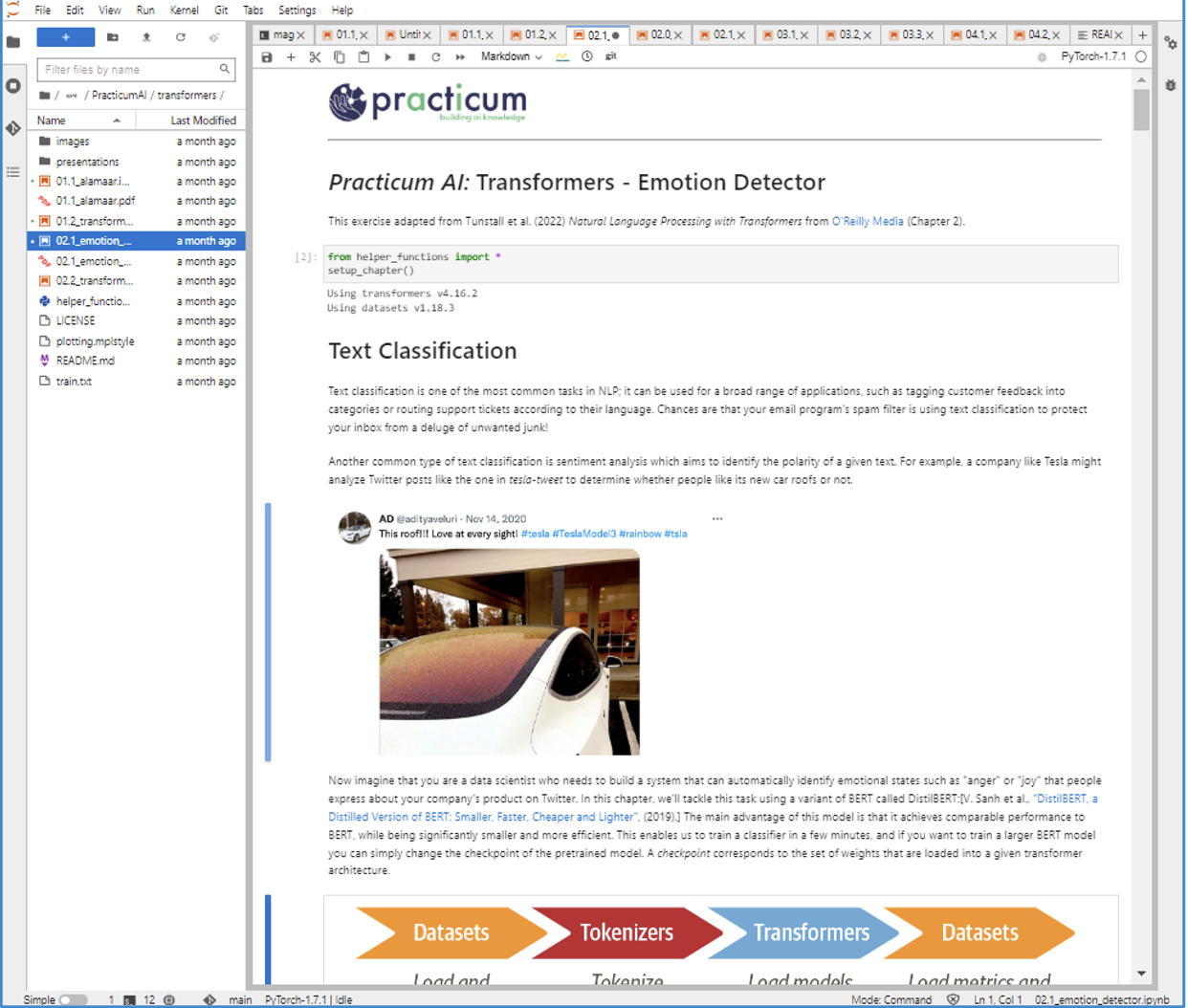 AI relies on computer code, and Jupyter Notebooks are the standard tool to develop and share AI and other data analysis code. The code is usually in the Python programming language, which we’ll cover in the next course, Practicum AI: Python for AI! Jupyter Notebooks are interactive, so you can see the results of your code as you change it, which facilitates the iterative processes involved in cleaning data, testing different models, and adjusting hyperparameters (model settings). Notebooks also allow you to add nicely formatted text and images to provide explanations, embed helpful graphics, and overall, enhance the user experience. Notebooks are also portable, so you can use them on your laptop or on a remote server. For these reasons and more, Jupyter Notebooks are a great tool not only for developing AI, but also for teaching you about AI, and that is why we will use Jupyter Notebooks extensively throughout the Practicum AI series of courses.
AI relies on computer code, and Jupyter Notebooks are the standard tool to develop and share AI and other data analysis code. The code is usually in the Python programming language, which we’ll cover in the next course, Practicum AI: Python for AI! Jupyter Notebooks are interactive, so you can see the results of your code as you change it, which facilitates the iterative processes involved in cleaning data, testing different models, and adjusting hyperparameters (model settings). Notebooks also allow you to add nicely formatted text and images to provide explanations, embed helpful graphics, and overall, enhance the user experience. Notebooks are also portable, so you can use them on your laptop or on a remote server. For these reasons and more, Jupyter Notebooks are a great tool not only for developing AI, but also for teaching you about AI, and that is why we will use Jupyter Notebooks extensively throughout the Practicum AI series of courses.
Git and GitHub.com
As noted above, code is at the foundation of AI. Being able to transparently and efficiently track code development, share code with others, and foster reproducibility are important features offered by using a type of software known as version control systems. Git is a version control system that allows you to track file changes over time. This makes it easy to collaborate with others on projects, revert to previous versions of your code, find bugs, test new ideas, and share reproducible results.
GitHub is a website that hosts git repositories (or collections of files). It is an excellent tool for AI development because it allows you to store, share, and deploy code. GitHub also has many collaboration tools, such as allowing you to track your progress on team projects, track and resolve bugs, host web pages, and more.
Leveraging similar technologies, model and dataset repositories allow seamless sharing and versioning of AI models and datasets. By sharing AI models and datasets, the time, effort, compute power, and energy consumed in training these models and developing the datasets can be leveraged for future research. While version control, git, and model repositories may seem like advanced tools, they are such critical parts of AI development that we feel they are essential tools for every AI practitioner to learn. By starting with these tools from the beginning, you will be well-positioned to continue using industry-standard tools as you continue your journey.
Computing Environments
High-Performance Computing (HPC) environments are essential for training large AI models. As we showed in the first course, rapid advances in AI in the 2010s and beyond were fueled by the recognition that the graphics processing units (GPUs) initially designed for gaming were ideal for the highly parallel computations used in training neural networks. Subsequent advances in GPUs specifically designed for AI applications have further increased capabilities. While these advances have driven amazing new applications of AI, they also mean that for most applications, specialized, and often expensive, computer hardware is needed for model training and deployment. Ultimately, this means what you can do on a standard laptop or desktop computer is limited when it comes to AI. For this reason, the Practicum AI courses are not intended to be run on your own computer.
Access to compute resources with advanced GPUs is one barrier that limits equitable access to AI technologies. Some companies, like Google, provide limited GPU access for free, but due to the hardware costs and power consumption, free tiers are often limited, and costs can quickly add up when doing AI model development and deployment.
HPC systems are generally composed of hundreds or thousands of servers, all networked together to operate as a single system. Access models vary, but many universities, government agencies, and companies have their own HPC systems for their needs. Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and others rent access to portions of their systems, generally called cloud computing. The key commonality among these systems is that they provide access to scalable compute power that far exceeds what could be done on standard personal computers.
For Practicum AI, we focus on two popular compute environments for our lessons: Google Colaboratory (or Colab) and using an HPC system. If you have access to an HPC system with GPU resources, this is likely your best option. The University of Florida’s HPC cluster is called HiPerGator (HPG) and is managed by UFIT Research Computing.
Use the following table to determine which compute environment will work best for you.
Table comparing the pros and cons of the Google Colab and HiPerGator AI compute environments.
| System | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
Google Colab |
- Free tiers - Easy setup - Easy for anyone to get an account |
- Limited compute resources - Can be more challenging to load data from git repositories |
HPC (e.g. HiPerGator) |
- Lots of compute resources available - Easy to integrate with git and update repositories and datasets |
- Investments required for researchers - Some setup needed - Requires an account with various limitations of availability |




